Material for speakers: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=Theory= | =Theory= | ||
<div><ul> | |||
<li style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: top;"> [[File:Zscenarios.png|thumb|top|Z dependence of µ → e conversion rates for some | |||
sample scenarios [https://www.snowmass21.org/docs/files/summaries/RF/SNOWMASS21-RF5_RF0-TF6_TF0_Heeck-043.pdf].]] </li> | |||
=PIP-II accelerator= | =PIP-II accelerator= | ||
Revision as of 22:49, 18 June 2021
Mu2e
Mu2e public results and material for speakers
Theory
-
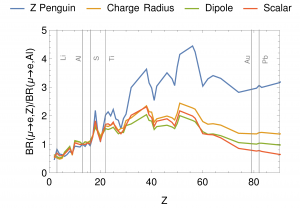 Z dependence of µ → e conversion rates for some sample scenarios [1].
Z dependence of µ → e conversion rates for some sample scenarios [1]. -
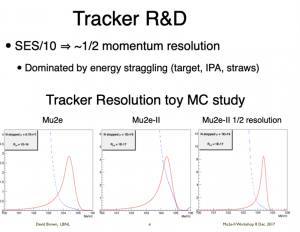 Slide illustrating the requirement on track resolution for Mu2e-II compared with Mu2e. Noe that the resolution has contributions from several sources. The blue dashed curve on each plot indicates the electron spectrum from muon decays in orbit (DIOs). The red curves show the conversion electron spectrum for the values of [math]\displaystyle{ R_{\mu e} }[/math] indicated in the legends.
Slide illustrating the requirement on track resolution for Mu2e-II compared with Mu2e. Noe that the resolution has contributions from several sources. The blue dashed curve on each plot indicates the electron spectrum from muon decays in orbit (DIOs). The red curves show the conversion electron spectrum for the values of [math]\displaystyle{ R_{\mu e} }[/math] indicated in the legends.